What Are Anatase and Rutile in Titanium Dioxide (Titanium oxide)?
Titanium Dioxide (Titanium oxide) is one of the most common white pigments used in a number of industries, including coatings, plastics, and inks. It exists in two principal forms of crystal structure- anatase and rutile titanium dioxide, and while both forms have the same chemical composition (TiO₂), they are distinct in crystal structure, appearance, and performance properties. These differences make rutile suitable in applications requiring high opacity, UV resistance, while anatase is suitable for applications where high brightness and photocatalytic properties are advantageous, such as in specialized coatings, road markings, and films.
1. Anatase in Titanium dioxide (TiO2).
Anatase has a tetragonal crystal structure, thus having a lattice that is more open and reactive. Appears as a whitish-blue powder and exhibits high brightness, very high brightness, very high light scattering, and great photocatalytic activity. Therefore, it is most desirable for.
- Crystal Structure: Tetragonal (i.e., a particular arrangement of titanium and oxygen atoms)
| Properties: | Applications: |
| If more chemicals get UV light, then they can perform better reactions, which makes them useful in photocatalysis (such as degrading pollution). | Photocatalysis: such as air purification, water treatment, and self-cleaning surfaces. |
| If the temperature is high, it transforms into rutile. It is less stable at high temperatures. |
Self-cleaning surfaces using TiO₂ coatings |
| Antase has more surface area, which causes a fast reaction. | Sometimes it is also present in pigments, and rutile is more present in these chemicals than it is in other chemicals. |
Available Grades of Anatase Titanium Dioxide –
SA-216 is a disposable anatase titanium dioxide grade characterized by purity and higher levels of whiteness, dispersibility, and active UV performance; along with its fineness of grind and high brightness, SA-216 is also suitable for different applications that require color consistency, smoothness of texture, and improved weathering performance.
This grade is usually used in the following markets:
- Paper Coatings – good opacity, whiteness, and smoothness.
- Road Marking Paints – brilliant reflectivity and permanence in brightness.
- Rubber Compounds – enhanced aging resistance and retained mechanical properties.
- Plastic Masterbatches – homogenous dispersion and color consistency over time between different polymers.
Anatase titanium dioxide is more commonly used in fairness compared to rutile types; thus, it is favored in formulations that prioritize surface quality along with wear to equipment. SA-216 anatase titanium dioxide can also function in self-cleaning and anti-bacterial applications from its photocatalytic activity.
The coatings, rubber, and plastics industries trust SA-216 for performance under understandable, economical terms.
2. Rutile in Titanium dioxide (Tio2)
- Crystal Structure: Tetragonal (structure is slightly compact and stable).
| Properties: | Application |
| It is more stable at high temperatures. |
Paints, plastics, and ink formulations using TiO₂ coatings |
| This makes it useful in industrial applications, and it is less reactive. | It is used for high-temperature applications such as welding rods. |
| It reflects more light, which makes it a good white pigment. And its refractive index is also high. |
Industrial-grade titanium dioxide powder |
Available Grades of Rutile Titanium Dioxide –
Sukhmani Impex has a full range of high-performance rutile titanium dioxide (titanium oxide) products that are well suited to a wide variety of industrial uses. These products are manufactured to ensure excellent opacity, brightness, dispersion, and weatherability for consistent results in finished products.
DR-2400 – RUTILE TITANIUM DIOXIDE
Applications: PVC, Powder Coating, Masterbatches
It is a rutile titanium dioxide grade designed for high opacity and excellent weather resistance. Its advanced surface treatment ensures:
-
Exceptional whiteness and gloss
-
Strong UV and chalk resistance
-
Superior dispersion and processing performance
Best suited for PVC profiles, thermoplastics, industrial powder coatings, and color masterbatches, DR-2400 protects the customer‘s ability to get high brilliance whiteness, durability, and extended years of performance in harsh environments.
DR-2100 – Versatile Rutile Titanium Dioxide Multi-Coating:
Application: Powder Coating, Wood Coating, Waterborne Coating, Road Marking Paint
Designed as a multi-purpose rutile grade for both solvent-based and waterborne coatings featuring:
- superior opacity and light fastness
- smooth dispersion and gloss retention
- resistance to yellowing and UV degradation
DR-2100 has been widely used for architectural coatings, powder coatings, wood finishes, and retro-reflective road markings, providing economical performance on many substrates.
DR-945 – General-Purpose Rutile Titanium Dioxide
Applications: Paint, Ink, PVC, Coating, Plastics
It is a general-purpose rutile TiO₂ pigment that has been developed with superior brightness and coloring strength. It offers:
- Good hiding power and durability
- Consistent particle size and dispersion
- Compatibility with a variety of resins and additives
DR-945 is popularly used in decorative paints, flexographic and gravure inks, PVC films and profiles, and coating plastics. DR-945 provides good performance for high-volume production runs and maintains balance across many performance characteristics.

Comparison Table: Anatase vs Rutile Titanium Dioxide Powder
| Property | Anatase | Rutile |
| Crystal Structure | Open structure, more reactive | Dense, stable structure |
| Stability | Less stable, becomes rutile at high temperature | More stable, especially at high temperatures. |
| Reactivity | Highly reactive (good at photocatalysis) | Low reactive (stable, good in pigments) |
| Band Gap | Wider Closed Gap (Better for Photocatalysis) | Narrow band gap (less useful in photocatalysis) |
| Applications | Photocatalysis, some solar cells, niche pigments | Main pigment (paint, coatings), welding rods |
| Optical Properties | Low refractive index (low light scattering) | High refractive index (better for pigments) |
Benefits of Anatase and rutile in tio2
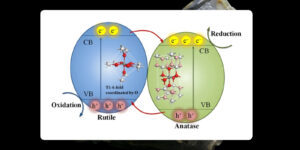
Anatase TiO₂ is perfect for environmental applications because of its strong photocatalytic activity and UV efficiency. Rutile TiO₂ is favored for pigments, sunscreens, and high-temperature applications due to its exceptional UV protection, thermal stability, and light-scattering capability. Both variants have different purposes.
Anatase to Rutile Transformation:
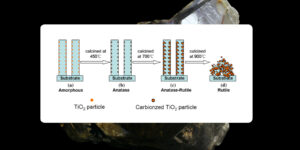
- Anatase is metastable and transforms into rutile when exposed to high temperatures (around 700°C). Rutile is more stable than anatase, so it is more commonly used in industrial applications.
It is exceedingly reactive and very effective at absorbing UV light, but it is a little less stable and mainly used for photocatalysis, such as cleaning pollutants, and in a few solar cells. Rutile, on the other hand, is more stable due to its crystalline structure and is used for pigments, such as in a wide variety of paints and coatings, and therefore is preferred for its best capability to scatter light.
For optimal performance, it is important to select the appropriate form and grade of TiO₂ powder for your application. If you are looking for highly reactive TiO₂ (specifically SA-216 high surface area anatase type) or a durable version of TiO₂ where it is used as a pigment in coatings (such as DR-2400 DR-2100 DR-945), your choice must fulfill your requirements regarding performance.
The aforementioned is especially true for industries that utilize high-performance TiO₂ coatings, such as plastics, paints, and inks as getting the proper grade will produce the best overall performance. Understanding the properties of these different TiO₂ forms certainly aids in achieving better durability, better brightness, and overall product performance.






