
Titanium Dioxide in Paint
Titanium Dioxide in paint. It’s the main synthetic white pigment, and it’s everywhere—in house paint, car finishes, you name it. What makes it so good? Well, it’s got a high refractive index, so it scatters light like crazy. That means you get bright, solid coverage—no streaks or see-through spots. The stuff hides whatever’s underneath, giving you that clean, crisp look people expect. Honestly, it’s been the secret behind bright, opaque paints for nearly a hundred years.
Applications
Silicone Paints

UV Coating
Silicate Paints
Powder Coatings
Emulsion Paints

Can Coatings
Industrial Coatings

Architectural Paints
Why is Titanium Doxide used in paint?
Titanium Dioxide in paint is an inorganic compound used as a white pigment. It gives paint its bright, crisp colour and makes sure it covers surfaces well. This stuff packs serious hiding power, so any old colour underneath disappears fast. It also holds up against sunlight and bad weather, which means paint lasts longer and keeps looking fresh.

Titanium Dioxide Powder for Paint
Titanium oxide powder matters in paint mostly because it covers so well and looks bright. You don’t need a ton of coats to hide what’s underneath—just a couple does the trick. It also helps paint last longer since it fights off UV rays, so colours don’t fade or break down quickly. On top of that, titanium oxide boosts the paint’s whiteness and makes colours pop, which works great for both protecting surfaces and making them look good. Its tiny particles and high refractive index give it an edge over other white pigments, so you see it used everywhere in paint.
High Hiding Power
- TiO₂ offers exceptional hiding power, allowing it to conceal the underlying surface effectively.
- This property ensures that the paint achieves the desired opacity and coverage.
Whiteness and Brightness
- As a fine white powder, TiO₂ imparts maximum whiteness to paints and coatings.
- Its brightness enhances the overall appearance of surfaces.
UV Protection and Durability
- As TiO₂ absorbs UV light, the underlying molecules of resin remain protected from UV damage.
- Its presence enhances the weather resistance of coatings, ensuring longevity.
Scattering of Visible Light
- TiO₂ efficiently scatters visible light due to its high refractive index.
- This scattering effect contributes to the reflective and bright nature of coated surfaces.
Selecting the Correct TiO2 Grade for Your Paints & Coatings
Choosing the appropriate grade of titanium dioxide for painting and coating products determines the performance characteristics you’ll be able to achieve from those products. Different grades of titanium dioxide have different characteristics, which affect how the product will perform when it is applied in a coating. Let’s review how to choose a titanium dioxide grade that will enable you to meet your goals:
Opacity and Hiding Power
People use TiO2 in paints and coatings mainly because it makes them opaque—it hides what’s underneath. TiO2 stands out because it has a really high refractive index compared to most stuff, so it scatters light better. That scattering is what makes the paint look solid and covers the surface, even if you don’t put on much. Since TiO2 does this job with less pigment than other options, it’s a smart pick for anyone making paint.
Brightness and Whiteness
TiO2 gives paints and coatings that bright, clean white everyone wants. It reflects a lot of visible light, so surfaces look crisp and fresh. When TiO2 is especially pure, the whiteness really stands out and makes everything look better. That’s why it’s so important for things like interior walls, car paints, and decorative finishes—anywhere you want a sharp, impressive look.
Choosing TiO2 Grade Based on Application
- Interior Paints: Prioritize brightness and whiteness. Anatase TiO2 may be suitable, but rutile with suitable surface treatments can also be used.
- Exterior Paints: Require high durability and weather resistance. Rutile TiO2 with inorganic surface treatments is ideal.
- Industrial Coatings: Depending on the specific requirements (e.g., chemical resistance, mechanical properties), choose rutile
TiO2 with appropriate surface treatments. - Specialty Coatings: For applications requiring specific properties like UV protection or high reflectivity, select TiO2 with tailored surface treatments.
Types of Tio2 for Paints and Coatings
There are two major forms of TiO2 used in paint and coating formulations:
Rutile Titanium Dioxide For Paint
Rutile TiO2 stands out as the most stable form. It’s tough, blocks light really well, and shrugs off bad weather. Those dense, tightly packed particles make coatings stronger, especially when you need them to handle sun, rain, and wear—think buildings, cars, or ships. Its hiding power is top-notch, so colors stay true and the coating holds up, even after years outside. That’s why you find it in so many architectural, automotive, and marine paints.
Anatase Titanium Dioxide For Paint
Anatase TiO2 stands out for its bigger surface area and lighter weight compared to rutile, which gives it that extra brightness and pure white look. But it doesn’t hold up as well over time — UV light wears it down faster, so it’s not the best choice for outdoors. You’ll find anatase TiO2 in indoor paints, decorative finishes, cosmetics, and even paper coatings, pretty much anywhere you want that bright, clean white without worrying about harsh weather.
How to optimize the use of titanium dioxide in Paint
Effective Dispersion of TiO₂ Particles
In order for TiO₂ pigments to achieve maximum efficacy, all primary particles must be utilised to their fullest extent. The ideal light-scattering properties are obtained when TiO₂ particles are thoroughly dispersed so that each individual particle is evenly distributed and not grouped in the same location.
The Dispersion Challenge: Separation and Stabilization
A major challenge in the dispersion process is that TiO₂ particles have a strong tendency to attract one another. This has two key implications:
Separation:
- Significant effort is required to separate these particles during dispersion.
- High-energy dispersion equipment is typically used for this purpose, such as:
1. Disk dispersers (dissolvers)
2. Pearl millsWhile disk dispersers can provide initial dispersion, the shear forces they generate are often insufficient to fully separate all primary pigment particles. More complete separation is generally achieved with a pearl mill, which applies higher shear forces.
Stabilization:
- Once separated, the particles need to be stabilized to prevent them from re-agglomerating, a process known as flocculation.
- Stabilization is achieved by adsorbing a stabilizer, or dispersant, onto the surface of the particles immediately after they are separated.
The dispersant works by ensuring that particles repel each other, maintaining separation. This can be achieved through two mechanisms:
- Electrostatic stabilization: All particles acquire the same electrostatic charge, causing mutual repulsion.
- Steric stabilization: Polymeric tails on the dispersant molecules dissolve in the surrounding liquid, creating a barrier that prevents the particles from coming back together.
Distributing the Particles
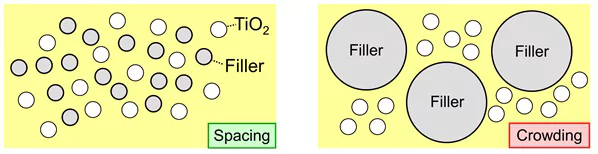
The ultimate goal is to distribute the stabilized TiO₂ particles evenly throughout the system. Optimal scattering efficiency is achieved when these particles are not only separated and stabilized but also spaced adequately within the medium.
Particles Distribution
Spacing:
- Ensuring adequate spacing between TiO₂ particles is essential. This can be achieved by combining TiO₂ with filler particles of a comparable size.
- Filler particles do not scatter light but help maintain the separation of TiO₂ particles, preventing crowding.
- Crowding occurs when filler particles are significantly larger than TiO₂ particles, leading to undesired clumping of TiO₂.
By carefully selecting filler particles that match the size of TiO₂ particles and adjusting their dosage, one can achieve optimum whiteness and hiding power of the TiO₂ pigment.
Safety Considerations
When it comes to using TiO2 in paints and coatings, safety really matters—for people and the environment. Breathing in fine TiO2 dust, especially during manufacturing or when you’re applying paint, can be a real problem. That’s why you need good ventilation and the right protective gear. TiO2 itself isn’t classified as a carcinogen, but there’s still some worry about it generating free radicals—particularly when it’s in the form of nano-sized particles. To cut down on that risk, companies often treat the surface of these particles to reduce their photocatalytic activity. As for disposal, you’ve got to follow the rules to make sure you don’t end up harming the environment.
Conclusion
TiO₂ is everywhere in the coatings world—it’s the go-to white pigment. It makes paints look bright and helps them cover surfaces better. Plus, it boosts durability, especially for paints that need to handle the outdoors. But here’s the thing: TiO₂ really does its best work when you get the formula and the process just right. Knowing how light bounces around inside the paint is key if you want that extra pop of brightness and coverage.
There’s more. TiO₂ soaks up UV rays, which protects the paint’s resin underneath from getting wrecked by sunlight. That’s a big deal for longevity. Still, chemists need to watch out for radicals forming where TiO₂ meets the resin, since that can cause its own problems. Tuning these details lets you really get the most out of TiO₂, giving you paint that not only looks good but lasts.
Sukhmani Impex gets this. They offer a wide range of TiO₂ grades, so you can find the right match for different paints and coatings. They focus on quality and consistency, so you get reliable results every time you print.
